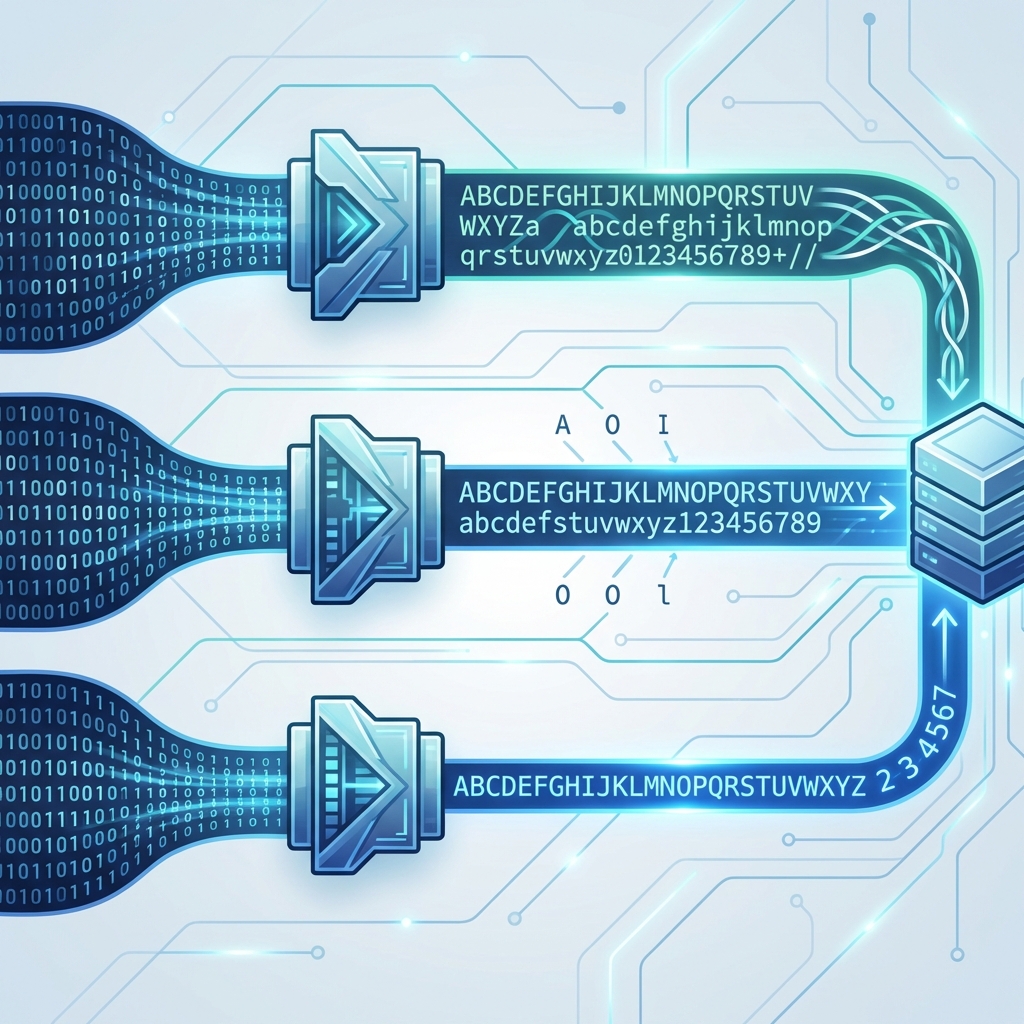
What is Base64 Encoding?
Base64 is an encoding scheme used to represent binary data using a set of 64 printable characters (A-Z, a-z, 0-9, +, /).
It is primarily used to transmit binary data safely over communication channels that are designed to handle only text, such as email attachments or image data embedded within JSON.
Why “64”?
Since one character can represent 64 different values (2 to the power of 6), data is processed in 6-bit chunks. By combining this with the standard 8-bit computer byte, it allows for a consistent conversion across different systems.
Other Encoding Schemes (Base58, Base32)
- Base58: Commonly used in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. It excludes similar-looking characters (like 0 and O, I and l) to prevent human input errors.
- Base32: Uses digits and a subset of the alphabet (32 characters total). Useful in case-insensitive environments like file systems or certain URLs.
Beware of “Data Overhead”
When you encode data in Base64, the size increases by approximately 33% (1.33x the original size).
Embedding large image files as Base64 strings in HTML or JSON can negatively impact page load speeds and API performance, so use it judiciously for small assets.
Common Use Cases
- Data URIs: Embedding small icons or assets directly into HTML/CSS.
- Basic Authentication: Encoding
username:passwordfor HTTP headers. - JWT (JSON Web Token): Formatting headers and payloads into a URL-safe string.
Encode/Decode with DevToolKits
Our Base64/58/32 Converter allows you to switch between different encoding formats and instantly see the results.
💡 Tip: When handling multi-byte characters (like Japanese or emojis), ensure you are using UTF-8 encoding before applying Base64 to avoid corruption.
